
Top page > New Initiatives
Innovative efforts to indirectly assume the costs of conserving biodiversity have emerged in recent years.
This section will discuss schemes devised by financial institutions which promote the greening of privately-owned land and corporate activities that consider biodiversity.
•Year started : July, 2008
•Location : Nagoya City, Aichi Prefecture
Nagoya City has lost 1,643 hectares of its green spaces[1] during the fifteen years between 1990 through 2005, in particular, those on privately owned land, which account for approximately two-thirds of the city area. In order to increase more green spaces on privately-owned land, in April of 2008, Nagoya became the first Japanese city to require greening on new construction or building enlargement sites. Under the program, owners are obligated to green a certain area of land according to the total site area.
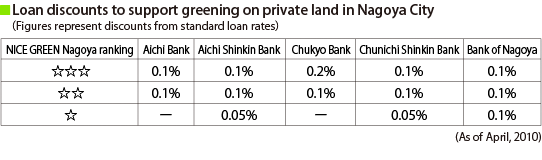
In July, 2008, local banks in Nagoya City in support of this program launched a new housing loan scheme to lower the interest rate for customers who engage in increasing green spaces on private land. The interest rate is determined based on rankings under the "NICE GREEN Nagoya" program[2], under which the city issues certification of the level of greening. The program has been applied to three loans as of August 20, 2010 and is expected to invite more customers to promote greening on privately-owned land in Nagoya City.
•Year started : November, 2009
•Location : Service area of local bank in Shiga Prefecture
In 2005, a bank, based in Shiga Prefecture, formulated the "Principles for Lake Biwa," which dedicates the bank to environmental conservation and sustainable local development by establishing standards for production, sales and services that will serve such purposes. Interested companies in support of the principles are rated based on fifteen items regarding environmental corporate activities, including ISO14001 acquisition, environmental accounting and greenhouse gas reduction. Based on these ratings (PLB ratings), companies may be entitled to loan discounts (PLB Fund).
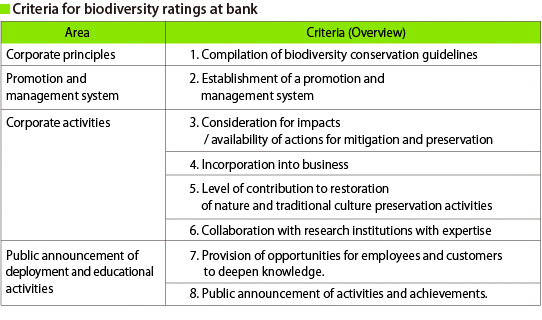
In addition, in November, 2009, the bank launched a new rating system incorporating a biodiversity perspective. These new ratings known by the name "PLB-BD ratings" grade corporate consideration for biodiversity on a scale of 1 to 100 points divided into five ranks, based on eight criteria under the four areas of: corporate principles, promotion and management systems, corporate activities, and public announcement of deployment and educational activities.
As of July 31, 2010, loans totaling 16 billion 961 million yen for 6,829 companies have been rated under the PLB ratings. More time is required to make performance data for PLB-BD ratings available. The bank has rated 1,200 customers based on the criteria for PLB-BD ratings and has notified customers of their ratings in order to raise awareness of the importance of preserving biodiversity and to increase knowledge of the new loan product among its customers.
[1] Land covered by green vegetation, including natural woods, planted woods, grass, agricultural land, rivers and ponds.
[2] A program under which greening on sites located in the city is assessed and rated by the city. It is a voluntary program, under which owners of building projects without greening obligations or existing green spaces can also apply for certification. Projects sites where the ratio of total green area to total site area exceeds the standard rate are graded based on certain criteria, namely 1) total area of green spaces; 2) ratio of trees compared to other vegetation on site; 3) greening of adjacent streets; 4) preservation of existing trees; 5) greening of rooftops and walls; and 6) efforts to maintain and manage green spaces. Ratings are determined according to grades: three-star for 80+ points, two-star for 50-80 points, one-star for less than 50 points. As of August 20, 2010, certifications for 283 sites have been issued since the program was implemented on October 1, 2008 (adopted on April 10, 2010).

